- Swiss Franc (Fr. )
- Euro (€)
- Czeck Koruna (Kč )
- Hungarian Forint (Ft )
- Polish Złoty (zł )
- Canadian Dollar ($)
- Mexican Peso ($)
- Norwegian Krone (kr )
- Chinese Yuan (¥)
- Indian Rupee (₹)
- Australian Dollar ($)
- New Zealand Dollar ($)
- Saudi Riyal (﷼ )
- UAR Dirham (د. إ )
- Bulgarian Lev (лв )
- US Dollars ($)
- GB Pound (£)
- Danish Koruna (kr )
- Romanian Leu (RON )
-
 CatalogTop All products in one place
CatalogTop All products in one place
-
 Software Defined RadioPopular Explore Signals Beyond Limits
Software Defined RadioPopular Explore Signals Beyond Limits
-
 RFID/NFC Unlock Possibilities with RFID/NFC
RFID/NFC Unlock Possibilities with RFID/NFC
-
 Antennas Antennas for every signal need
Antennas Antennas for every signal need
-
 Amplifiers Signal Boosters & LNAs
Amplifiers Signal Boosters & LNAs
-
 Radio Communication Radio Communication Essentials
Radio Communication Radio Communication Essentials
-
 Test & Measurement Unleash Precision. Reveal Signals.
Test & Measurement Unleash Precision. Reveal Signals.
-
 FPGA DevelopmentNew Accelerate Ideas. Build Hardware.
FPGA DevelopmentNew Accelerate Ideas. Build Hardware.
Receiving Satellite Imagery with RTL-SDR v4
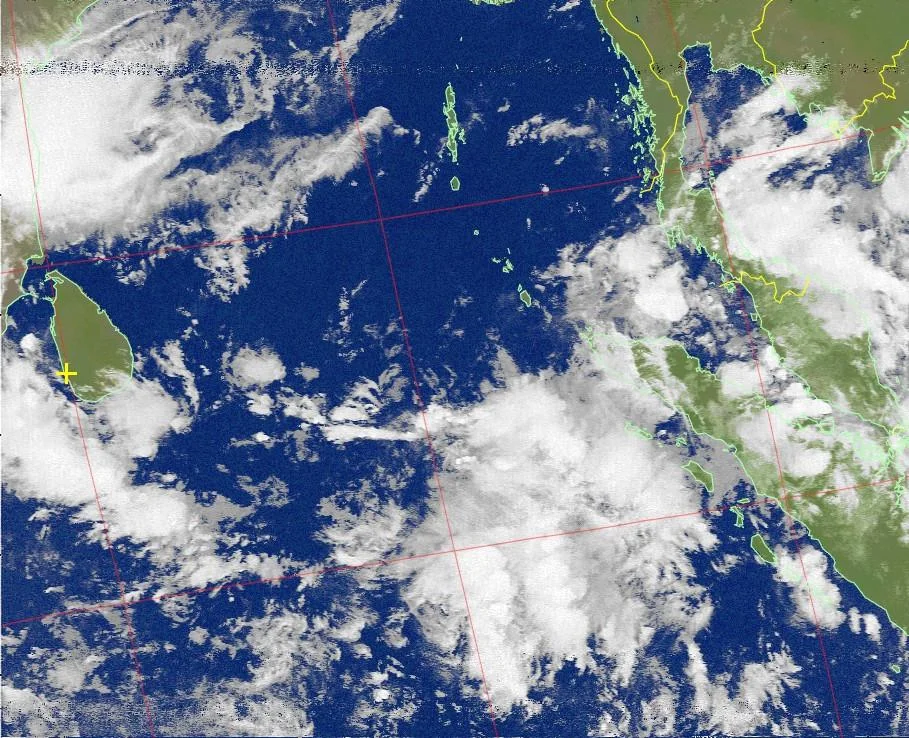
Have you ever dreamt of receiving images directly from satellites orbiting Earth? With a little technical know-how and the affordable RTL-SDR v4, that dream can become reality! This guide will walk you through everything you need to capture fascinating satellite imagery, from gathering the necessary software to decoding the signals.
Required Software:
- SDRSharp:This free and versatile software acts as the control center for your RTL-SDR v4. Download it from the official SDRSharp .
- WXtoImg:This free software decodes the raw audio captured by SDRSharp and transforms it into viewable satellite imagery. You
- GPredict (Optional):While not essential, GPredict is a handy tool that predicts satellite passes over your location. This helps you plan your reception windows and maximize your chances of capturing clear images. You can find GPredict on the AMSAT website
Additional Hardware:
- RTL-SDR v4: This Software-Defined Radio (SDR) dongle is the workhorse of your setup. It picks up the faint radio signals transmitted by satellites.
- Antenna: A good antenna designed for receiving weather satellite frequencies (around 137 MHz) is crucial. A simple dipole antenna or a commercially available NOAA satellite antenna will work well.
Step-by-Step Guide:
Setting Up SDRSharp:
- Install SDRSharp and connect your RTL-SDR v4 to your computer.
- Launch SDRSharp and familiarize yourself with the interface.
Tuning In:
- Use GPredict (or online resources) to identify upcoming NOAA satellite passes over your location. Note the frequency mentioned for the specific satellite.
- In SDRSharp, set the "Frequency" to the designated NOAA satellite frequency (usually around 137 MHz).
- Adjust the "Sample Rate" to 2.048 MS/s for optimal reception.
- Set the "Mode" to "WFM" (Wideband FM).
- Adjust the "Gain" to achieve a clear signal without overloading.
Capturing the Signal:
- Once the satellite is within range, you should see a distinct Doppler shift (wavering sound) on SDRSharp's display.
- Click the "Record" button in SDRSharp to capture the raw audio data as the satellite passes overhead.
Decoding the Image:
- Open the recorded audio file in WXtoImg.
- Select the appropriate satellite and reception mode in WXtoImg.
- Click "Start" to begin the decoding process. WXtoImg will convert the audio data into a grayscale satellite image.
Congratulations! You've successfully captured your own satellite imagery. With practice and experimentation, you can refine your technique and capture even clearer images.
Additional Tips:
- Experiment with different antenna designs for improved signal reception.
- Pay attention to weather conditions; clouds can obstruct the satellite signal.
- Various online communities and forums dedicated to SDR enthusiasts offer valuable resources and troubleshooting tips.
The World Awaits:
By following these steps, you've unlocked the door to a fascinating world of satellite imagery. Witnessing real-time weather patterns, cloud formations, and even glimpses of Earth's surface from space adds a whole new dimension to the world of radio reception. So, grab your RTL-SDR v4, tune in, and capture your own piece of the satellite image universe!
© 2023 - 2025 SDRstore.
